Best Knee Replacement Hospital in Ahmedabad
If your knee is severely damaged by arthritis or injury, it may be hard for you to perform simple activities, such as walking or climbing stairs. You may even begin to feel pain while you are sitting or lying down.
If nonsurgical treatments like medications and using walking supports are no longer helpful, you may want to consider total knee replacement surgery. Joint replacement surgery is a safe and effective procedure to relieve pain, correct leg deformity, and help you resume normal activities.
The knee is the largest joint in the body and having healthy knees is required to perform most everyday activities. The knee is made up of the lower end of the thighbone (femur), the upper end of the shinbone (tibia), and the kneecap (patella). The ends of these three bones where they touch are covered with particular cartilage, a smooth substance that protects the bones and enables them to move easily.
The menisci are located between the femur and tibia. These C-shaped wedges act as "shock absorbers" that cushion the joint. Large ligaments hold the femur and tibia together and provide stability. The long thigh muscles give the knee strength. All remaining surfaces of the knee are covered by a thin lining called the synovial membrane. This membrane releases a fluid that lubricates the cartilage, reducing friction to nearly zero in a healthy knee.
Normally, all of these components work in harmony. But disease or injury can disrupt this harmony, resulting in pain, muscle weakness, and reduced function.
CAUSE
The most common cause of chronic knee pain and disability is arthritis. Although there are many types of arthritis, most knee pain is caused by just three types: osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and post-traumatic arthritis.
Osteoarthritis. This is an age-related "wear and tear" type of arthritis. It usually occurs in people 50 years of age and older, but may occur in younger people, too. The cartilage that cushions the bones of the knee softens and wears away. The bones then rub against one another, causing knee pain and stiffness.
Rheumatoid arthritis. This is a disease in which the synovial membrane that surrounds the joint becomes inflamed and thickened. This chronic inflammation can damage the cartilage and eventually cause cartilage loss, pain, and stiffness. Rheumatoid arthritis is the most common form of a group of disorders termed "inflammatory arthritis."
Post-traumatic arthritis. This can follow a serious knee injury. Fractures of the bones surrounding the knee or tears of the knee ligaments may damage the particular cartilage over time, causing knee pain and limiting knee function.
DESCRIPTION
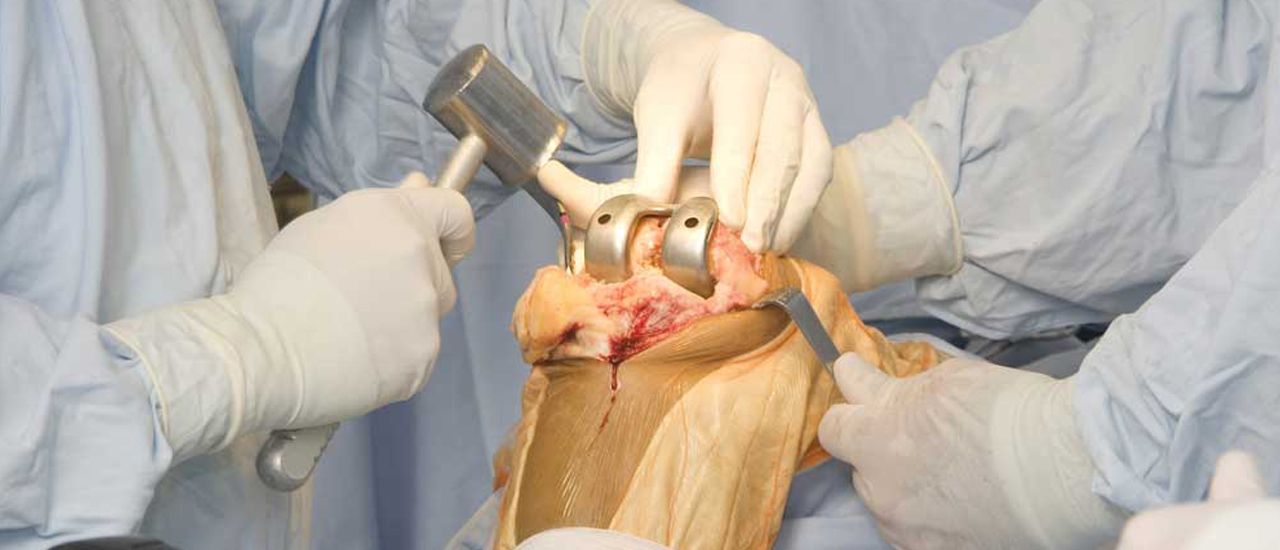
A knee replacement (also called knee arthroplasty) might be more accurately termed a knee "resurfacing" because only the surface of the bones are actually replaced.
There are four basic steps to a knee replacement procedure.
Prepare the bone.The damaged cartilage surfaces at the ends of the femur and tibia are removed along with a small amount of underlying bone.
Position the metal implants.The removed cartilage and bone is replaced with metal components that recreate the surface of the joint. These metal parts may be cemented or "press-fit" into the bone.
Resurface the patella. The undersurface of the patella (kneecap) is cut and resurfaced with a plastic button. Some surgeons do not resurface the patella, depending upon the case.
Insert a spacer. A medical-grade plastic spacer is inserted between the metal components to create a smooth gliding surface.
SURGERY
ANESTHESIA
After admission, you will be evaluated by a member of the anesthesia team. The most common types of anesthesia are general anesthesia (you are put to sleep) or spinal, epidural, or regional nerve block anesthesia (you are awake but your body is numb from the waist down). The anesthesia team, with your input, will determine which type of anesthesia will be best for you.
PROCEDURE
The procedure itself takes approximately 1 to 2 hours. Your orthopedic surgeon will remove the damaged cartilage and bone, and then position the new metal and plastic implants to restore the alignment and function of your knee.
HOW YOUR NEW KNEE IS DIFFERENT
Improvement of knee motion is a goal of total knee replacement, but restoration of full motion is uncommon. The motion of your knee replacement after surgery can be predicted by the range of motion you have in your knee before surgery. Most patients can expect to be able to almost fully straighten the replaced knee and to bend the knee sufficiently to climb stairs and get in and out of a car. Kneeling is sometimes uncomfortable, but it is not harmful.
Most people feel some numbness in the skin around your incision. You also may feel some stiffness, particularly with excessive bending activities. Most people also feel or hear some clicking of the metal and plastic with knee bending or walking. This is a normal. These differences often diminish with time and most patients find them to be tolerable when compared with the pain and limited function they experienced prior to surgery.
PROTECTING YOUR KNEE REPLACEMENT
After surgery, make sure you also do the following: